Blog
The Mosquito Life Cycle
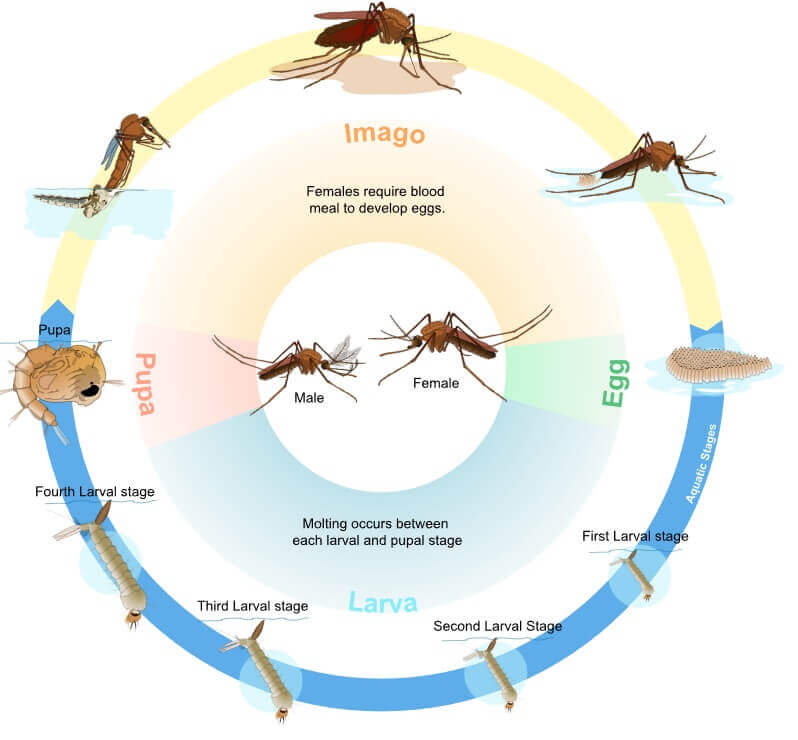
The mosquito life cycle may only begin in an aquatic environment. The female mosquito lays between 50 and 100 eggs on the water’s surface, and so it begins. While both male and female mosquitoes feed on nectar, only the female mosquito feeds on blood in order to produce her offspring. Male mosquitoes live for around two weeks, while females live from three weeks to several months, and can lay around 500 eggs during its life span.
The Mosquito Life Cycle
A female mosquito’s eggs will hatch within 24 hours and will develop into larvae. Mosquito larvae or “wigglers” must breathe air to survive; hence they remain on the water’s surface and feed by filtering small particles from the water. They will occasionally dive down to the water for nutrition, or to escape from predators. During this stage, the larvae will moult approximately 4 times and grow rather quickly. Pupae or “tumblers” breathe air through two tubes located on their back. It’s from inside the pupal lining that mosquitoes emerge as adults within two days. They will rest on top of the water until they are strong enough to fly, at which time they will look for food.
Kinds of Mosquitoes that Breed Around the Home
The presence of mosquitoes in your neighbourhood does not necessarily mean that they are breeding close by because mosquitoes have the capacity to fly far distances from their breeding grounds. However, the mosquito life cycle can also begin in your own home.
The most common sort of mosquito is the Culex pipiens. It thrives on the water that contains organic wastes and the females feed mostly at night on birds, which makes them the main carriers of the mosquito-borne viruses. Another common species of mosquito is the Culex restuans, which females usually lay their eggs in the same kinds of locations as the Culex pipiens, but don’t usually feed on humans.
Ways to Control Breeding Sites
Female mosquitoes are usually selective when choosing a site to lay their eggs, seeking clean and still water in the wild. However, several kinds of mosquitoes that breed in residential areas will tolerate polluted water. Therefore, it’s necessary to eliminate all standing water on your property, including water in bamboo pole holder, buckets, flower pots, children’s toys, and any long-standing puddles. Repair all leaks on faucets, hoses to ensure that no water collects. If the water source is cut off and dries up during the developmental stages of the insect, the mosquito life cycle will be disrupted.
To achieve good mosquito control in Singapore, a mosquito larvicide can be purchased. Larvicides contain chemicals that eliminate the mosquito in its immature stages and halt the mosquito life cycle in its tracks. These chemicals are called methoprene and Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis (BTI). However, since mosquitoes have the capacity to fly far from their breeding grounds, you may experience pest problems without having a breeding ground nearby. Additionally, there are effective mosquito repellent products for lawns and vegetation specifically intended for use on adult mosquitoes. These chemicals go by the names of cyfluthrin, lambda-cyhalothrin, and permethrin, and can be applied to shrubs, low tree limbs, shaded areas under decks, and along the dwelling’s foundation. Most come in sprays and have to be re-applied periodically for maximum efficiency. Be sure to use insecticides exactly as indicated on their labels.

Pingback: Mosquitoes & Rain - What's the Connection?
Pingback: Eliminate Mosquitoes - Repellent and Other Safety Measures
Pingback: Things That Eat Mosquitoes